다음 글은 인프런의 무료 강의를 요약 정리한 내용입니다
[무료] LLM Application 개발 경험 공유회 - 인프런 | 강의
LLM Application 개발을 위한 기본 배경지식과 개발 경험을 공유합니다., 5월에 진행한 LLM Application 개발 지식 & 경험 공유회를 업로드합니다! LLM Application을 개발하시는 분들에게 조금이라도 도움이
www.inflearn.com
찾아보니 유튜브에도 똑같은 내용으로 올라와 있다
링크 : https://www.youtube.com/live/TJ2mYNpUTAY?si=lQsgGqbAZm7k10TR
처음엔 가볍게 듣고자 했는데
생각보다 너무나도 알차서 어느순간 필기하고 있는 나자신을 발견...
찾다보니 유튜브에도 많은 강의가 있던데..
다음엔 LangChain을 다룬 강의도 들어 볼까함,,
1. LLM Base Knowledge
LLM(Large Language Model)은 현재 NLP분야에서 가장 주목
- 트랜스 포머 기반(Decoder Only)모델이 대세
- 상용으로는 ChatGPT4 , PaLM2
- 오픈 소스가 열심히 추격중 (요샌 falcon?)
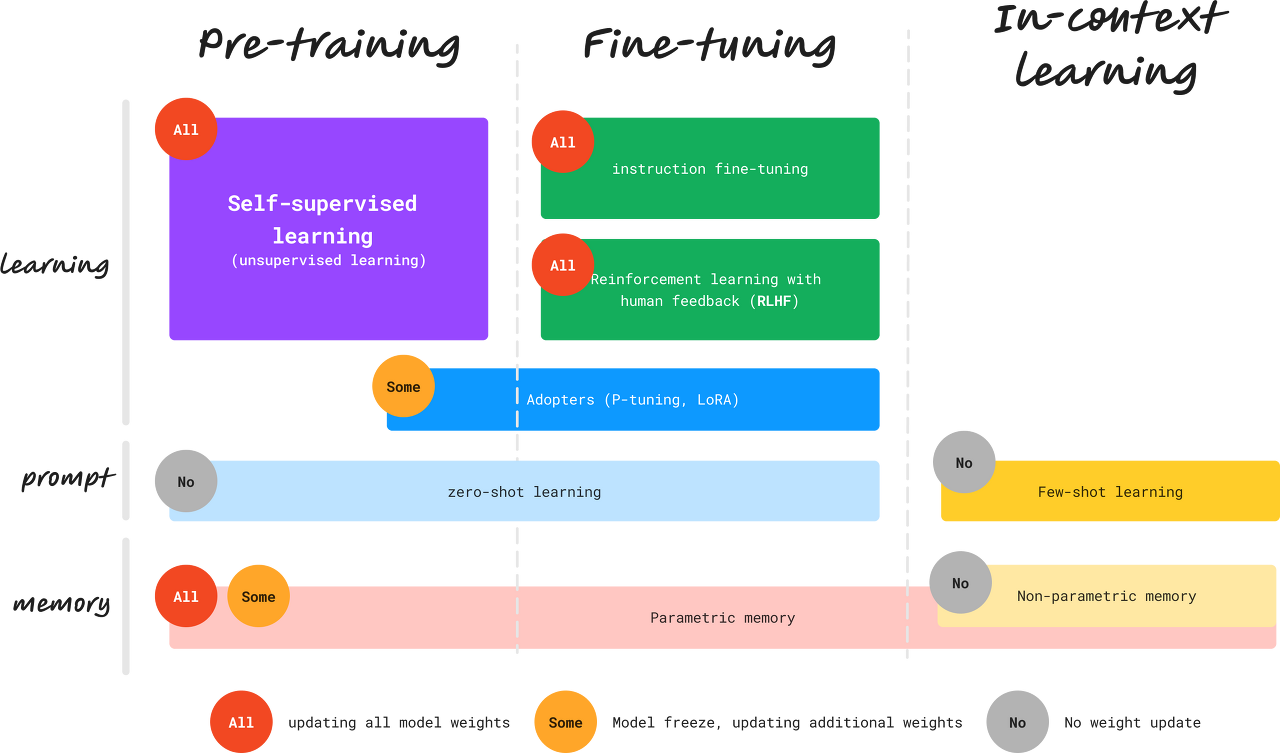
Fine-Tuning
- Pre trained Model(like ChatGPT)을 용도에 맞게 튜닝하는 것
- Instruction fine tuning -> RLHF(Reinforcement Learning with Human Feedback) -> Adaptor(P-tuning,LoRA) 방식으로 발전!
- 오픈 소스 LLM 기반 파인 튜닝이 얼마나 퍼포먼스가 잘 나오는지는 아직 모름
- ChatGPT는 gpt-3.5-turbo, gpt-5모두 Fine Tuning API
In Context Learning
- 우리 모두 열심히 하고 있는 Prompt Engineering이 바로 이것
- 별도의 모델 가중치 업데이트를 시키지 않고 명령 프롬프트 내에서 원하는 대답을 얻게 하는 것
- X-Shot Learning, Chain-of-Thought, Self-Consistency 등의 여러 기법들 존재
2. LLM Application (RAG)
LLM Application 이란?
- 기존 애플리케이션: 코드를 통해 결정적인(Deterministic) Rule Base 기반으로 동작함
- LLM 애플리케이션 : 비결정성이 포함된(지멋대로의) LLM의 추론 결과를 바탕으로 동작함
- LLM은 사람 수준의 추론을 가능하게 해줘서 기존에 가지고 있던 문제를 수비게 풀어 줄 수 있음
(추천,분류,챗봇,AI어시스턴스)
LLM Application 간단 플로우
1) 클라이언트의 입력이 들어온다
2) 미리 설정한 프롬프트에 질문을 넣어서 LLM에게 요청한다
- 필요한 경우 질문에 필욯나 데이터를 포함시킨다
- 외부 API, 데이터베이스, VectorDB 등
3) 요청 결과를 바탕으로 새로운 프롬프트,함수를 실행한다(Chaining)
4) 최종 결과가 나오면 답변으로 반환한다.
사실 현재 대부분은 결국 Private/Public 데이터를 기반으로 대답을 해주는 방식으로 LLM Application 개발중
- 고객센터 챗봇
- 법률 판례 검색
- 주식 리포트 생성
이는 RAG( Retrieval Augmented Generation) 이라고 하는데, 사용자 Input에 수집된 데이터를 합께 프롬프트에 담아 질문하는방식
-> 결국 본질은 1. 질문에 필요한 데이터를 최대한 잘 뽑아서 2. LLM이 잘 대답해 줄 수 있도록 하는 것
<Data Retrieval>
유저 질문(Input)에 답변할 떄 필요한 정보를 가져오기 위해서 여러가지 방법이 있음
1. 외부 API 활용
- search api (google search , bing...) -> 비쌈
- web scraper
- Saas API (Slack , Notion)
- Document loading (PDF,CSV, ...)
보통 Search API를 활용해서 답변의 신뢰도를 높이는 경우가 많음 (하지만 비쌈)
LangChain, LlamaIndex, Unstructured 같은 오픈소스들에서 많이 지원해줌
2. Structured 데이터베이스 활용
- Data Warehouse(BingQuery, Snotflake, ...), RDBMS
- 서비스 운영에 필요한
- 질문을 엔진에 질의할 수 있는 SQL 형태로 변경 필요 (LLM 에게 요청하기)
1) Question to LLM : 1주일 전 테슬라 가격 알려줘
2) LLM Answer : SELECt ticker, price FROM stock_price WHERE create_at = '2023-06-07 00:00:00'
3) Action : RDBMS에 쿼리
3. 키워드(Keyword) 기반 혹은 전문(Full Text) 검색
- Elastic Search , Solr , OpenSearch 등
- 기본적으로 많이 알려진 검색 엔진들 활용하기
- Saas(Algolia) 형태로 제공해주는 엔진을 사용하는 것도 빠른 시도에 도움이 될듯
4. 유사도 기반 검색 ( Similarity Search) *** 문맥의 유사도 분석
- 두 벡터의 거리를 기반으로 유사도를 측정함
- 일반적으로 텍스트를 임베딩(Enbedding)시킨 벡터로 변환하여 거리 기반 유사도를 검사
- 임베딩 모델을 통해 텍스트를 벡터로 임베딩하게 됨
- 임베딩된 벡터들이 들어간 데이터베이스를 VectorDB라고 함
- VectorDB는 벡터간 유사도 검색을 내부에서 지원해줌
- 사용자는 그냥 API로 손쉽게 검색만 하면 됨
5. VectorDB는 현재 크게 게임 체인저는 없음. 다 비슷비슷함
- Chroma, FAISS (테스트 환경, Evaluate 등의 로컬 환경에서 돌릴 때 유용)
- Pinecone, Milvus, Weaviate 같이 요새 핫한 친구들도 나옴
- Elastic Search, Redis 처럼 범용 데이터베이스에서 지원해주기도 함
결국 유사도 검색의 핵심은 질문의 벡터와 답변의 벡터가 잘 연결 될 수 있도록 Embedding 하는 방식이 중요
- Embedding API로 openAI에서 제공하는 Embedding API 많이 사용자
- OpenAI Embedding API의 가격이 75% 저렴해짐
- Embedding Model도 계속 발전하고 있으니 계속 지켜봅시다
6. 우리는 Pinecone 사용
- 선택한 가장 큰 이유는 직관성 + 쉬운 사용 (Free Trial 제공부터 하면서 넘어옴)
- Hybrid Search(Metadata Filter) + Upsert도 지원
- 다만 Saas 형태로만 지원하고 Self Hosting이 안되는 건 아쉬움
<Data Retrieval Tips>
7. 사실 검색 결과를 높이기 위해선 Semantic Search + Keyword Search 를 함께 적용하는 게 좋음
- 일반적으로 검색을 통해 다양한 후보군을 가져온 후 ReRanking 하는 작업 진행함 (구글도 그렇다고..)
Cohere가 요새 뜬다는데 쓰는 것도 고려중(API 비용이 막 저렴한 건 아니라서 고민중)
- 전통적인 검색 엔진 방법(Keyword , full text) + 유사도 검색을 함께 사용해서 정확도를 높이는 것이 좋음
https://txt/cohere.com/rerank
8. Vector DB 매칭 확률을 높이기 위해서 여러가지 시도를 해보는 것도 의미가 있음
텍스트 데이터를 어떤 방식으로 넣을건지 고민해보자
1)어떻게 쪼개서 넣을거니?
- Chunk Size, Overlap 여러 개로 테스트 해보기
- Pinpecone은 ChunkSize를 256~512 Token Size 로 추천함(OpenAI Embedding model)
2) Input을 어떻게 넣을 것인가?
- 질문이 복잡하다면 쪼개보자! decompose
- input 을 답변처럼 가공해서 쿼리하는 HYDE 방식도 있음
( 테슬라 얼만지를 답변으로 반환하게 해서 답변을 가지고 유사도)
9. Embeddubg 방식을 바꿔보는 것도 테스트 해봐도 좋음
- 실제 벤치마크 점수 기준으로 openAI의 text-embedding-ada-002를 이기는 임베딩 모델들 나옴
- 하지만 편하게 쓸 수 있는 건 아직까지 OpenAI Embedding이 짱(cohere는 어떤지 궁금)
https://huggingface.com/spaces/mteb/learderboard
10. 다양하게 VectorDB 인덱스를 구성하면서 테스트를 해보는 게 중요
뒷단에서 데이터를 빠르게 넣고 + 멱등하게 관리할 수 있는 Data Engineering infra 필요
<LLM Library>
11. LLM Application을 구성하기 위해서 필요한게 생각보다 있다
- Prompt 템플릿 + 변수관리
- 다양한 외부 데이터 접근(API)
- Vector DB Embedding + Search
- (이전에 답변에 컨텍스트가 필요하다면) Short Term memory
- (복잡한 태스크 수행이 필요하다면) Agent
- ...
현재 LangChain, LlamaIndex, Semantic Kernel 오픈 소스들이 나오고 있음
12. LLM Library(LangChain)
- LangChain이 LLM Application 개발에서 가장 많이 쓰임
- LLM과 통신하며 수행하는 작업 단위를 Chain으로 만들어서 관리
- Vector DB 관련 인터페이스가 가장 직관적이고 깔끔
- Pyhton, Javascript 모두 지원
- LangChain 생태계 + 커뮤니티가 가장 활발하다
- Awesome-langchain에서 이모저모 볼 수 있음
https://github.com/kyrolabs/awesome-langchain
- 근데 다큐먼트 솔직히 너무 불칠절하다
- Pinecone에서 런북 만든게 설명 잘되어 있음 (https://www.pinecone.io/learn/langchain)
- Langchain에 뭐가 많기는 하지만 결국 유즈케이스에 맞게 직접 커스터마이징 하게 됨
- LangChain이 좋은 건 뛰어난 확장성
- 우리는 우리 용도에 맞게 커스터마이징 많이 해서 사용중
- 여러 용도에 맞게 custom chain을 만들어서 사용자
- Conversational Ceontext를 유지하게 위해 Custom Memory(서비스 DB와 통신)를 만들어 구현
- LLM 결과 모니터링을 위해 Custom Callback 구현해서 메타데이터, 지표 모니터링
13. LLM Library (Llama Index)
- LangCahin과 유사하게 LLM Application 개발 올인원 툴로 사용 할 수 있음
- Index라는 단위로 데이터를 구조화 시켜 쿼리를 용이하게 함
- 다양한 Index(VectorStore, Tree, Knowledge Graph 등)을 지원함
- 즉 기존 데이터 소스를 더 효과적으로 찾을 수 있도록 인덱스 방식을 지원해줌
- 다양한 Query Engine을 지원해서 Index에 질의하는 방식을 다양화 함
- 복잡한 질문을 쪼개서 질문하기
- 확실히 Langchauin에 비해서 Data Retrieval 하는 과정과 Post Processing을 잘 지원해줌
- Langchain과 꽤 겹치는 부분이 있기도 하고 확실히 Retrieval 쪽에 강점이 있음
- 그러나 도입하려다 제외함. Langchain에 비해 러닝커브가 높고 Index management하기 쉽지 않음
- 여러 기법들을 적용하는 게 과연 얼마나 퍼포먼스 향상에 동무이 될지는 모르겠음 -> 결국 모두 실험해 봐야하는 데 이것 또한 비용
- Data Retrieval에 대한 퀄리티 고민을 더하게 될 때 도입 다시 해볼듯
14. 복잡합 유즈케이스
- 하나의 프롬프트에 많은 역할과 추론 과정을 요구할 때, 원하는 대로 말을 안들을 때가 많음
- 만약 이게 가능한 모델이 있다 하더라도(gpt-3.5는 우선 아님) 좋은 Prompt를 만지는 데 시간을 꽤 투자해야함
- 미국 주식 Q&A 챗봇 예시
1). 질문 유형에 따른 다양한 요구사항이 있음
- 시황을 물어볼 경우 시의성 중요함
- 특정 주식의 Fundamental 정보를 물어볼 경우 해당 정보에 접근하는 API 활용하기
- 질문이 여러 문맥을 포함하고 있을 수 있음
- 최근 3개월 간 가장 수익률이 높은 주식의 PER은 몇이야?(질문금지!)
2) 해결 방법( 두방식을 보통 같이 활용하곤 )
가. 프롬프트의 역할을 명확하게 해서 쪼갠 후 Chaining하기
나. Retrospective 하게 추론 & 실행을 반복하는 Agent 활용하기( 반복적으로 물어보기)
15. Chaining하기
- Contol flows with LLMs
- https://huyenchip.com/2023/04/11/llm-engineering.html#part_2_task_composability
- Sequential / Parallel / If / For loop
- 프롬프트를 Chaining하여, 개별 단계에서 답변의 정확도를 높이기 (우리는 파이프라인이라 부름)
- 다만, 답변 생성 시간/토큰 비용이 Trade-off + 초반 프롬프트에서 답변이 이상하면 downstream으로 에러가 전파될 수 있음
- 파이프라인을 잘 구성하기 위해서는 엔지니어링 리소스가 많이 들어감
- 예외처리, 유닛테스트/E2E테스트 모두 진행해봐야 함
- 우리 팀도 여러 파이프라인을 구성하여 답변 퀄리티를 높이기 위해 E2E테스트를 수시로 진행함
16. Agent (LLM에게 계속 반복적으로 물어봄..)
- Agent : 목표와 사용가능한 도구를 주면 스스로 행동하도록 하는 방식 혹은 아키텍처 혹은 코드 구현체
- 외부 리소스(구글 서치, Open API, 기타 API 등)를 활용해서 복잡한 태스크를 수행해야 할 때 유용함
- AGI(Artificial General Intelligence)를 구현하는 기본적인 방식임 auto gpt-3
쉽게 설명하면 아래와 같이 동작함 ( recursive 하게 동작함)
1) LLM에게 미리 정의한 툴(Search, VectorDB , 외부 API등)을 알려주고 질문에 대답하기 위해 툴을 선택하게 한다
2) 선택한 툴을 코드로 실행해서 결과를 얻는다
3) LLM에게 결과를 주고 질문에 충분히 대답할 수 있는지 물어본다. 만약 충분히 대답이 되면 결과 반환 후 종료
4) 대답이 안되면 답변에 필요한 새로운 질문을 생성해 1-3 반복
- Auto-GPT, BabyAGI, Jarvis(HuggingGPT)등 다양한 아키텍처이자 구현체가 존재함
- 다만 위 친구들이 얼마나 활용도가 높은지는 모르겠음(구현체인 만큼 자유도가 떨어짐)
- Agent를 사용하려면 자유도를 높게 가져갈 수 있는 Langchain을 활용하는 걸 추천함
- Langchain으로 autoGPT 구현한 코드도 있음( https://python.langchain.com/en/latest/use_cases/autonomous_agents/autogpt.html )
- Agnet는 Action의 Full Cycle이 LLM의 추론으로 돌아가는 방식임. 따로 운영시 테스트/디버깅이 힘들 수 있음.
충분히 잘 검토해보고 도입 필요가 있음
- 개인적으로는 예측 가능한 솔루션을 만들려면, Agent보다는 Prompt Chain + Rule Base(if-else 같은)로 가져가는 게 더 나아보임
17. 운영에서 신경 쓸 것
유저 인터페이스를 어떻게 가져가냐에 따라 기능적 요구사항이 달라짐
1) 챗봇 형태인가?
- 응답 Latency가 중요 -> Streaming 구현
- 이전 대화를 바탕으로 대답할 것인가? -> Memory 구현
2) 사용자가 어떻게 사용할 수 있는가?
- Quota가 따로 없다면 ChatGPT의 경우 Rate Limit을 신경 써야함
- 백그라운드에서 Bulk로 돌리는 경우가 많으면 OpenAI Organization 추가하는 게 좋음 API 두개로 들고?
- 인증이 없다면 외부 공격에 취약할 수 있음(다 돈이다!)
3) LLM Application 운영시 주요 metric
- Token Size
- First touch latency : 얼마나 답을 빠르게 시작했나
- Last touch latency : 얼마나 답을 빠르게 종료 했냐
4)후행 지표로 답변 Quality도 체크해야함
- 답변에 대한 Evaluation을 하는 파이프라인을 뒷단에 구성하는 것도 방법
5) 답변 퀄리티에 대해서 지속적으로 Evaluation하고 Quality Control 필요
평가 기준을 세우고 일관된 템플릿으로 답변 결과에 대한 퀄리티 비교 및 제안
6)Data Ingestion Infra 고민해봐야함
- 결국 원본 데이터를 보관하기 위한 Stage(Data Warehouse, 운영 DB 등)를 두고 용도에 맞게 Ingest 시켜야함
- 워크플로우 툴(e.g Airflow)을 적용하는 게 추후 좋을 수 있음
18. 느낀점
- 해당 애플리케이션을 개발한다는 것은 AI Engineering + Data Engineering(+MLOps) + Backend
- Engineering 이 적절하게 섞여는 느낌
- 생각보다 답변을 제대로 하는 LLM Application을 만들기까지 노력이 꽤 들어감
- LLM 답변에 대한 퀄리티와 신뢰성을 높이기 위한 작업이 쉽지 않음
- 결국 답변 퀄리티를 높이기 위한 Ops 환경 구성이 생각보다 비용이 들음 (MLOps와 유사)
- 결국 LLM Application의 품질은 답변과 직접적으로 연결되어 있음. 답변 퀄리티를 높이기 위해선 Data Retrieval이 제일 중요한 것 같음
- 프롬프트를 계속 만지는 것보다 질문에 적합한 Data를 가져오도록 하는 게 더 나을수도
- 더 나은 답변이 나오도록 계속해서 실험해봐야함 이를 위한 실험 환경도 구성되어야함
3. LLM OPs
1.LLM을 위한 MLOps 환경
- LLM : 언어를 출력으로 하는 대규모 딥러닝 모델
- MLOps : ML기 1. LLM을 위한 MLOps 환경
- LLM : 언어를 출력으로 하는 대규모 딥러닝 모델
- MLOps : ML기반 애플리케이션 수명 주기를 관리하는 전체 환경
- 이미 학습된 LLM이 있다는 전제 하에 환경이 구성되었다는 점에서 MLOps와 다름
- 실험 측면에서도 MLOps는 모델의 아키텍처, 하이퍼 파라미터, 데이터 보강을 집중
- LLMOps는 프롬프트, 파인튜닝을 주로 봄
<LLM Ops 란?>
2. LLMOps는 무엇을 가능하게 하는가
1) LLM 관련
- Foundation Model 선택
- Fine tuning
2)Prompt Engineering
- 프롬프트 별 버저닝 및 히스토리 관리
- 프롬프트 실행
3)Enxternal data Management
- Test Data Set (보통 Q&A 셋)
- Vector DB (& Embedding)
4)Evaluation
- 프롬프트, 파이프라인(Prompt Chained)결과 평가
- 유저 피드백 루프
- A/B Testing
5)Deployment
- Prompt, 파이프라인 배포
- LLM Metric 모니터링
3. Tool 소개
- Vellum
- HoneyHive
- FlowGpt, langflow ,flow eyes : prompt 끼리 chaining
4. 오픈소스/ Saas 보면서 느낀점
1)뭔가 하나를 딱 쓰고 싶지만, 다 애매함. 펀딩받고 있느 ㄴ단계의 서비스들이 많다 보니 아직까지 성숙도가 떨어짐
- 프롬프트 테스트 후 배포해도, 결국 배포된 api 하나만 사용하는게 아님
- 보통 프롬프트간 Control Flow가 적용된 파이프라인이 필요함
- +파이프라인이라는 작업 단위에 대한 Fine grained 설정이 필요함
- Visual Interface로 프롬프트를 체이닝 하는 경우, 중간에 output을 transform하는 경우들이 존재함
- External Data Management(VectorDB, Others...)에 대한 환경 제공은 아직 부족함
2)사내 LLMOps 툴 개발
- OpenAI Playground 에서 계속 테스트 하는건 더이상 힘들다고 판단
- 결국 인하우스 툴이 필요하다고 느껴져, 최소한의 기능으로 어드민 개발
거시적인 관점에서 하나의 질문도 여러번 해보는 것이 좋다 (매번 다른 답이 나오므로)
5. 느낀점
- 초반에 만들어둔 노력대비 아주 잘 사용하고 있음
아무리 못해도 프롬프트 버저닝, 배치실행 기능은 꼭 필요한듯. 지금이 가장 낫다는 보장이 없음
조금 더 예측 가능하고 정량적으로 평가를 진행하는 게 중요
- 이게 더 나을거 같아요 X
- 테스트에서 이런 경향성을 보이고 있어요. 이어서 ~~~을 설정해서 운영중인 프롬프트와 비교해볼게요 O
다만 하나의 프로덕트를 만드는 느낌이라 비용이 꽤 들어갈 수 있는 걸 고려해야함
- DB 설계부터 버저닝, 배포 환경 격리 등 신경써야 할 게 꽤 많음
4.Prompt Engineering
1.
- 영어로 작성하기 (한글로 쓰고 ChatGPT로 번역해서라도 넣으세요)
- 간결하게 + 명확하게 작성하기
- 프롬프트 Instruction 문단에 대한 구분은 $$$ , """" 같은 구분자로 명확하게
- 예제를 넣자
- 하지 말라고 하기보단 하라고 하는게 나음
2. X-shot Learning : 예시를 주면서
단순한 프롬프트일수록 적용해줄 때 효과가 좋음
zero-shot , one-shot, few-shot : 예제를 넣어라
3. Chain-of-Thought : 생각하는 과정 넣기 추론 하게 하기
CoT와 X-Shot은 보통 함께 쓰는 게 좋음
우리도 기본적으로 CoT + X-Shot 활용함(아예 팀에서 사용할 템플릿 만드는 것 추천)
4.Self-Consistency
LLM의 비결정적인 문제를 해결하기 위해 여러 번 돌려서 결과 채택하기
비용 측면에서 비효율적(우린 안씀)
다만 Data Retrieval을 할때 비슷한 방식을 적용해보는 시도는 가치가 있을지도
5. Tree-of-Thought
Tree 형식으로 후보 추론 -> 선택 -> 탐색을 반복하면서 최적의 답을 찾는 방식
근래 나온 Prompt 기법 중 퍼포먼스가 가장 높다고함
하지만 꽤 많은 비용(시간+돈)이 Trade-off
https://github.com/kyegomez/tree-of-thoughts
6. ChatGPT
결정성 관련
- 결정성(Determinitsic)을 높여야 하는 경우 Temperature, Top P를 낮게(0이 거의 기본값) 반면
창의적인 콘텐츠라면 Temperature나 Top P를 높게 가져가는 게 좋음
- OpenAI에서는 temperature와 top_p를 함께 만지는 것을 권장하지 않는다고 함
- 답변이 긴 경우, 반복을 줄이기 위해 Frequency Penalty를 높이는 것 권장
- 개인적으로, 출력 토큰이 많지 않은 경우에는 Temperature만 조절해도 충분했음
- ChatGPT 서비스의 gpt-3.5 모델과 gpt-3.5-turbo API는 다름. Gpt-3.5-turbo API 성능이 더 안좋음
- 따라서 API를 사용하는 경우 ChatGPT 서비스가 아닌 OpenAI Playground로만 테스트 해야함
- gpt-3.5-turbo가 text-davinch-003(Complete)와 10배 저렴+효율이 비슷하다고 했는데 잘 모르겠음
text-davinch-003가 거의 대부분 결과를 더 잘 만들어줌
- gpt-3.5-turbo-0301의 경우 System Message보단 User Message 쓰라고 권장
(gpt-3.5-turbo에서 system message에 대한 개선이 얼마나 되었는지는 모르겠음)
7. Hallucination
제일 중요한 건 Ground Truth를 잘 쥐어주는 것
시점에 대해서 제약사항을 주는 것도 좋음
- 답변의 신뢰성이 중요한 유즈케이스에서는 여러 조건으로 프롬프트를 옥죄는 게 나아보임
- ex1. 정말 맞는 지 다시 한번 생각하게 하기
- ex2. 인용을 달게 하기
- 물론 옥죄는 만큼 신뢰성을 높아지지만 답변의 다양성은 낮아질 수 있음
(그럼에도 불구하고 Hallucination이 종종 발생함)
- PaLM2 같이 최신 정보를 바탕으로 대답이 가능한 모델을 쓰거나 ChatGPT4를 쓰는 것도 좋음
- 하지만 결국 직접 파인튜닝 하지 않을거라면, 댇바에 필요한 Ground Truth 소스들을 잘넣어 주는 게 퀄리티에 갖아 큰 영향을 끼침
- 결국 데이터를 잘 가져오자!
8. 프롬프트 평가(Evaluation)
우리가 만든 프롬프트는 정말 나은걸까?
1) 정답이 있다면?
- 정답이 객관식이라면 Equal Check
- 정답과 얼마나 유사한지 ChatGPT에게 물어보기
- 정답과의 유사도(Embedding)를 통한 점수화
- 사람이 측정
2) 정답이 없다면?
- 프롬프트 간 비교 결과를 메트릭으로(자동화)
- 사람이 측정(평가 기준을 명확하게 세우기)
프롬프트를 평가하면서 느낀건데,
- 프롬프트에 역할, 규칙이 많아질수록 말을 안듣는다
- 즉, 몇개 돌려보고 끝내는게 아니라 충분하 데이터 셋을 여러번 돌려보자
- 동일한 질문도 여러 번 돌려보는 것도 방법
- 포맷에 대한 확인도 꼭해보기
(이번 OepnAI Update에서 ChatGPT가 Structured format을 지원한다고 함)
9. 프롬프트 관리
팀에서 프롬프트를 관리하려면, 애초에 기본적인 포맷에 대한 템플릿은 Source of Truth로 잡고 가는 게 낫다
(가독성도 가독성이지만 프롬프트를 처리하는 코드-레벨에서 편리함)
10. 느낀점
- 프롬프트에 정답은 없다. 너무 개별적인 것들에 집중하면 머리아픔(거시적으로 봐야함)
- 프롬프트 엔지니어링은 어느정도만 잘해놓고 다른일 하는게 나을수도
- LLM의 성능이 계속 더 발전하니, 우리가 고민하는 프롬프트 엔지니어링 이슈들이 금방 해결 될수도 있다.
- Hallucination의 본질적은 문제는 결국 Ground Truth를 잘 줘야함. 즉, Input에 해당하는 정보들을 잘 가져오는게
프롬프트를 튜닝하는 것보다 답변 퀄리티가 더 잘나올 수 있음
'DEVELOP > Backend' 카테고리의 다른 글
| LangChain 이란? (2) | 2023.12.04 |
|---|---|
| jsonString의 다형성 (feat. Gson) (0) | 2022.04.05 |
| [JUnit/Spring] Mockito annotion 차이(@Mock , @MockBean , @Spy , @SpyBean) (0) | 2021.10.27 |
| [Spring] DataAccessException 이란? (Spring의 예외처리 - 사라진 SQLException) (0) | 2021.05.20 |
| [Spring] @RestControllerAdvice , @ExceptionHandler 로 예외 처리하기 (0) | 2021.05.20 |